Achilles tendon ultrasound diagnostic imaging.
Preferred imaging method for Achilles tendon injury.
Issues with the Achilles tendon can occur for a variety of reasons including sporting injuriesy, overuse, age related degeneration, underlying inflammatory conditions, unsupportive footwear and abnormal foot biomechanics.
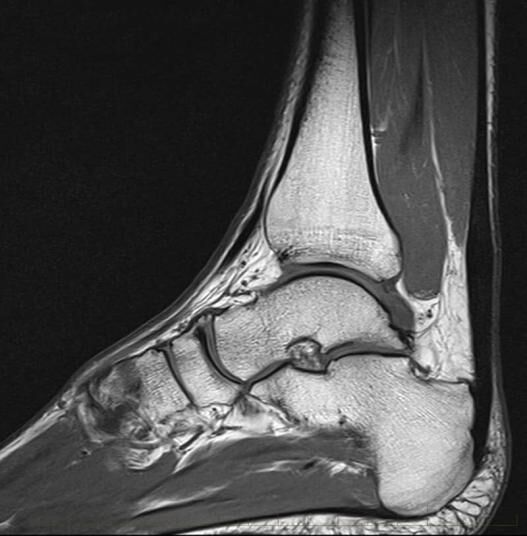
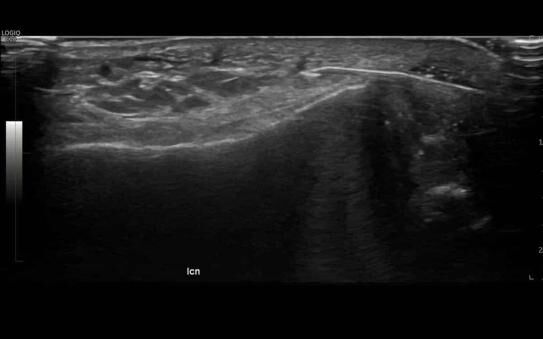
In many cases, your doctor will request you undergo medical imaging to assist them to diagnose the issue. While Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can be used to diagnose and assess most foot and ankle injuries including Achilles tendon conditions, ultrasound is often the preferred method as it is widely available, quick, reliable and cheaper than MRI.
Detailed imagery for an accurate diagnosis.
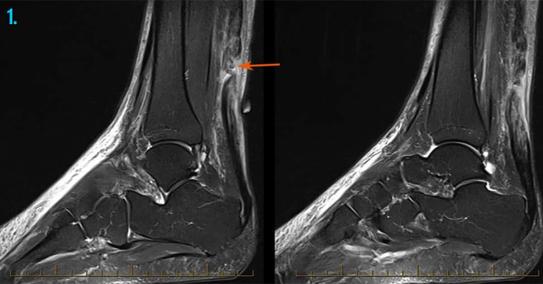
Whilst full thickness rupture of the Achilles tendon are well known for their dramatic loss of function, often seen in elite athletes, other and more common conditions include inflammation of the sleeve of connective tissue surrounding the Achilles tendon – the paratenon and may therefore result in paratenonitis (also known as peritendinitis or paratendinopathy). Chronic weakness and degeneration of the Achilles tendon (tendinosis or tendinopathy) often results from overuse as well as degeneration. Enthesopathy (that is to say, tendinosis at the bone – tendon junction) is often associated with retrocalcaneal and retro-Achilles bursitis.
An Achilles tendon ultrasound will allow your doctor to visualise the underlying anatomic structures as well as their quality, with the ability to quickly formulate as diagnosis and determine the severity of the injury.
Safe and radiation-free.
Unlike X-ray which uses ionising radiation to produce diagnostic images, ultrasound is completely radiation-free. Utilising inaudible high-frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of internal structures, ultrasound is a fast, painless and non-invasive diagnostic imaging method that can produce excellent results.
Further Information.
We welcome referring doctors to discuss the individual imaging needs of their patients with our radiologists.
Specialist Radiologists.
MSK & MRI Fellowship Trained Radiologists