Ultra Low Dose CT Scan Medical Imaging.
Melbourne Radiology Clinic has recently installed the latest generation CT Scanner that utilises an ultra low radiation dose to acquire diagnostic images, in some cases (particularly in the limbs), lower than a conventional digital X-ray.
With the advent of multi-slice (or multi-detector) technology, Computed Tomography (CT) is now a routine diagnostic imaging modality that is versatile and reliably answers many referring doctor’s clinical questions.
A CT scanner uses an X-ray beam that revolves around a patient to produce a cross sectional-image known as a ‘slice’. Modern CT scanners use multi-slice technology, which means that many fine slices may be performed of the patient as they enter the CT scanner in a single rotation, with the processing of the data resulting in reconstruction of the image from any angle. This means that 3-D images may be produced and assist in the formulation of a diagnosis. The current CT scanner used at Melbourne Radiology Clinic utilises an ultra low radiation dose to acquire diagnostic images, in some cases (particularly in the limbs), lower than a conventional digital X-ray!
Computed Tomography - Role in Diagnostic Imaging.
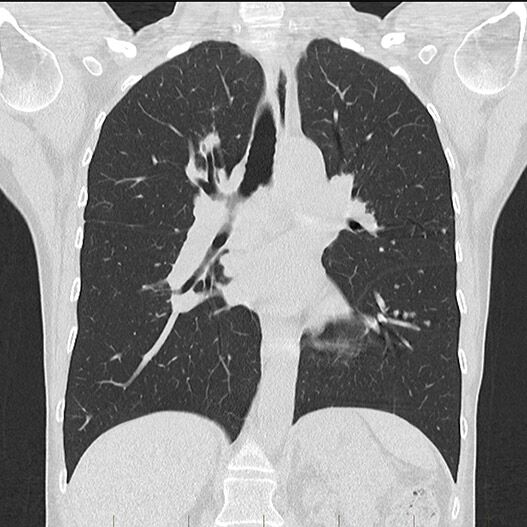
Computed Tomography (CT) is of particular use in the diagnosis of chest, abdominal and pelvic disorders, including the bowel and lungs, as well as in the production of images of arteries (known as an angiogram).
A CT angiogram can therefore be used to diagnose a brain aneurysm, blockage (stenosis) of an artery, including the arteries of the heart and of the legs. Importantly, the diagnosis of a life threatening blood clot to the lungs, known as a pulmonary embolus, is reliably made.
Multi-slice CT is also a suitable modality for evaluating the spine.
Patients unable to have an MRI scan may undergo either a CT and/or Ultrasound in order to further investigate their symptoms.
As a CT uses rapid X-ray technology, it can also be used for sophisticated spine injection procedures, as well as guiding a needle deep into body parts for a specific medical purpose, such as a biopsy or drainage.
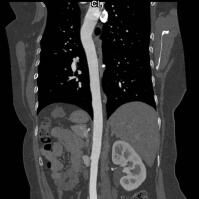
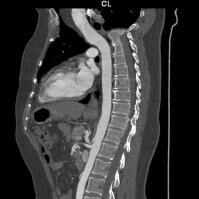
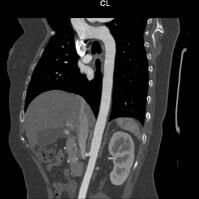
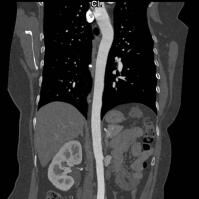
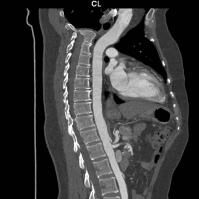
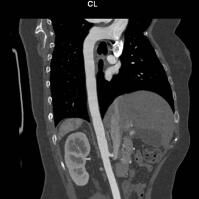
CT angiogram of the thoracic aorta.
CT angiogram of the thoracic aorta demonstrates excellent opacification of the aorta. The aorta in this case is of normal calibre.
Abnormalities of vessels that can be detected with CT imaging include (a). stenosis (blockage) of its lumen that can lead in interruption of blood supply to a particular area of the body, as well as (b) weakness of the wall that may to dilatation (aneurysm formation) and therefore potentially rupture (often fatal, especially in large arteries).
Our latest generation
ultra-low dose CT scanner
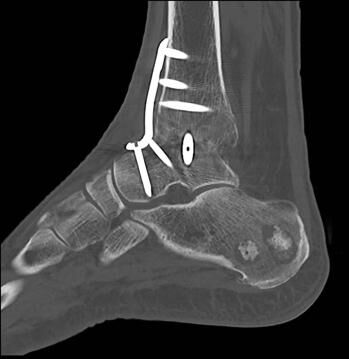
In 2019, Melbourne Radiology Clinic introduced the latest generation ultra-low dose CT scanner that delivers a significantly lower dose whilst at the same time maintaining image quality. This has particular applications in musculoskeletal and orthopaedic imaging, as the dose received in imaging small peripheral joints is comparable, if not lower, than digital X-ray. Imaging of prosthetic joints and other metallic surgical hardware is markedly improved, as well as significant reductions in dose during interventional procedures.
CLINIC DIRECTOR
Metal artefact reduction technology.
MRC’s low dose CT is able to scan patients that have an existing prosthesis or other post-operative metalware or on the opposite side without any significant loss of image quality for the symptomatic side that is intended on being replaced.
Further Information.
Referring doctors are welcome to discuss with our radiologists the imaging needs of their patients and whether a CT Scan is suitable for their patient’s medical condition.
Specialist Radiologists.
MSK & MRI Fellowship Trained Radiologists