Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a medical procedure also alternatively known as radiofrequency denervation (RFD), radiofrequency neurotomy (RFN), radiofrequency thermolysis, and rhizolysis.
Nerves transmit pain and in certain medical conditions, the function of these nerves can be disrupted in order to alleviate or at least minimise pain.
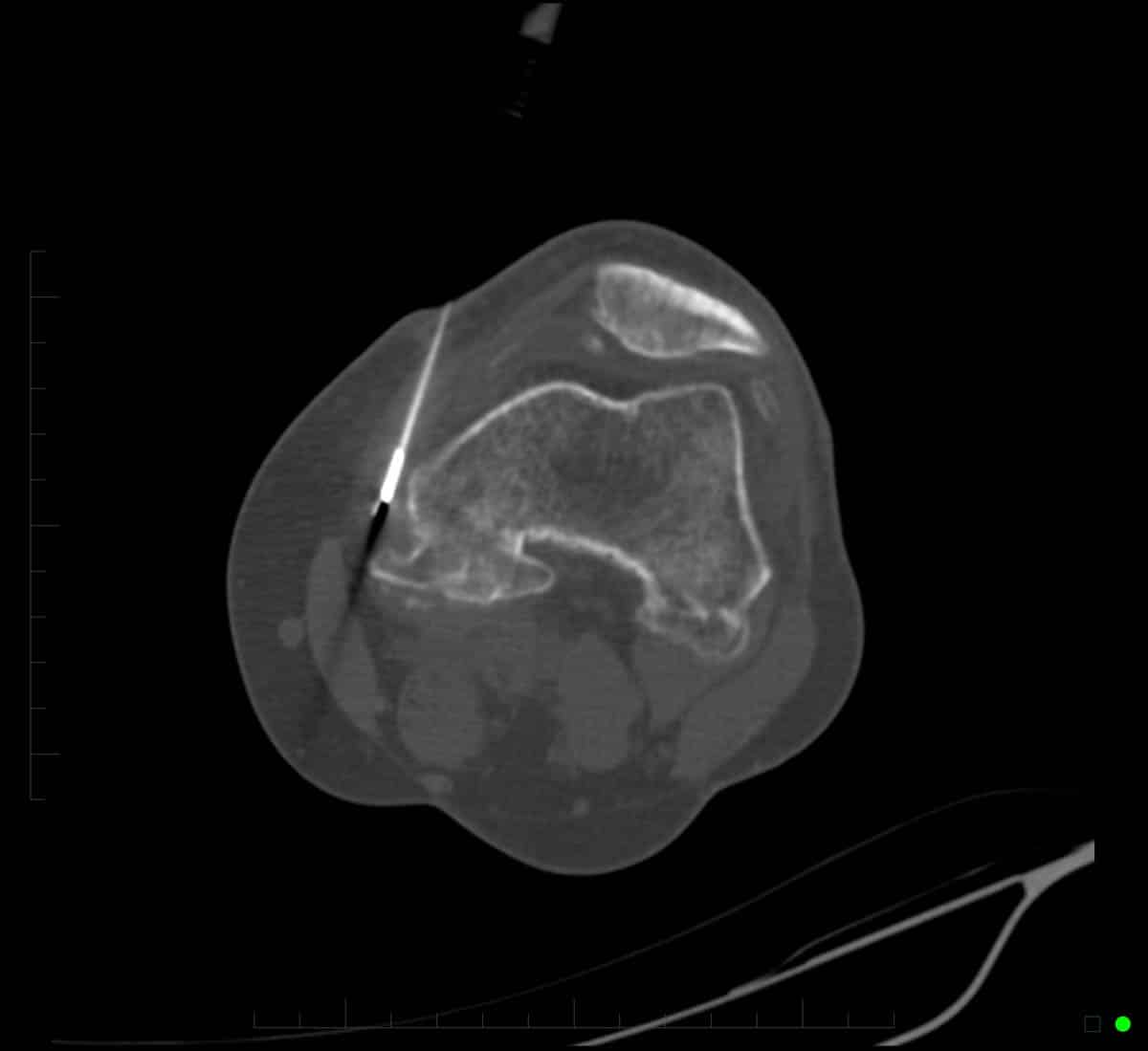
The procedure of RFA involves inserting a needle near the nerve that is proven or suspected to be the cause of the patient’s pain. A probe is inserted through the bore of the needle which is then heated, destroying the nerve.
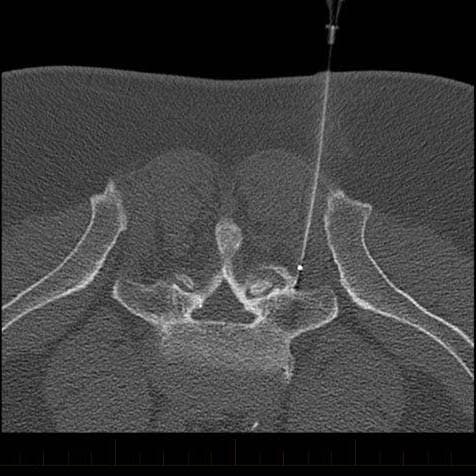
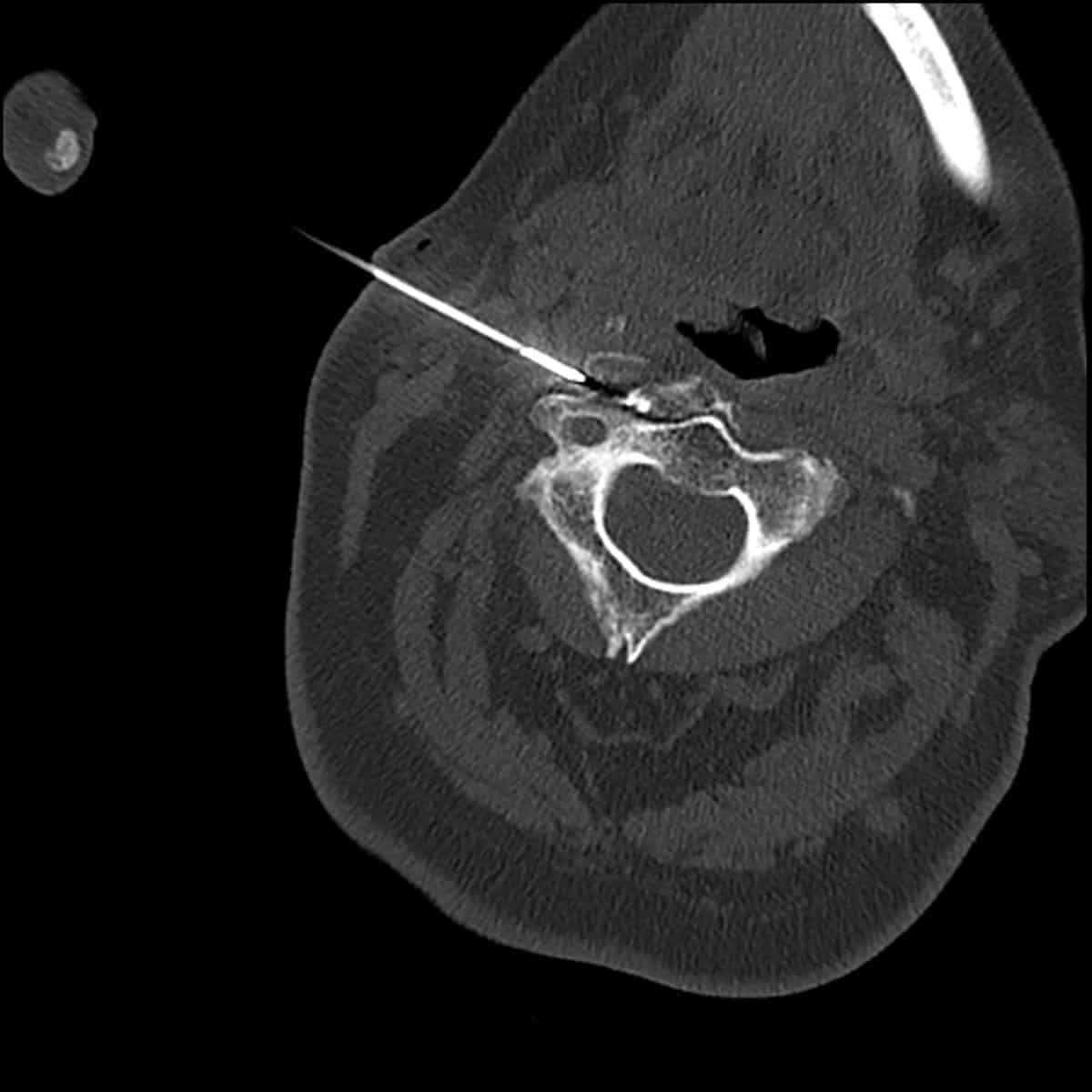
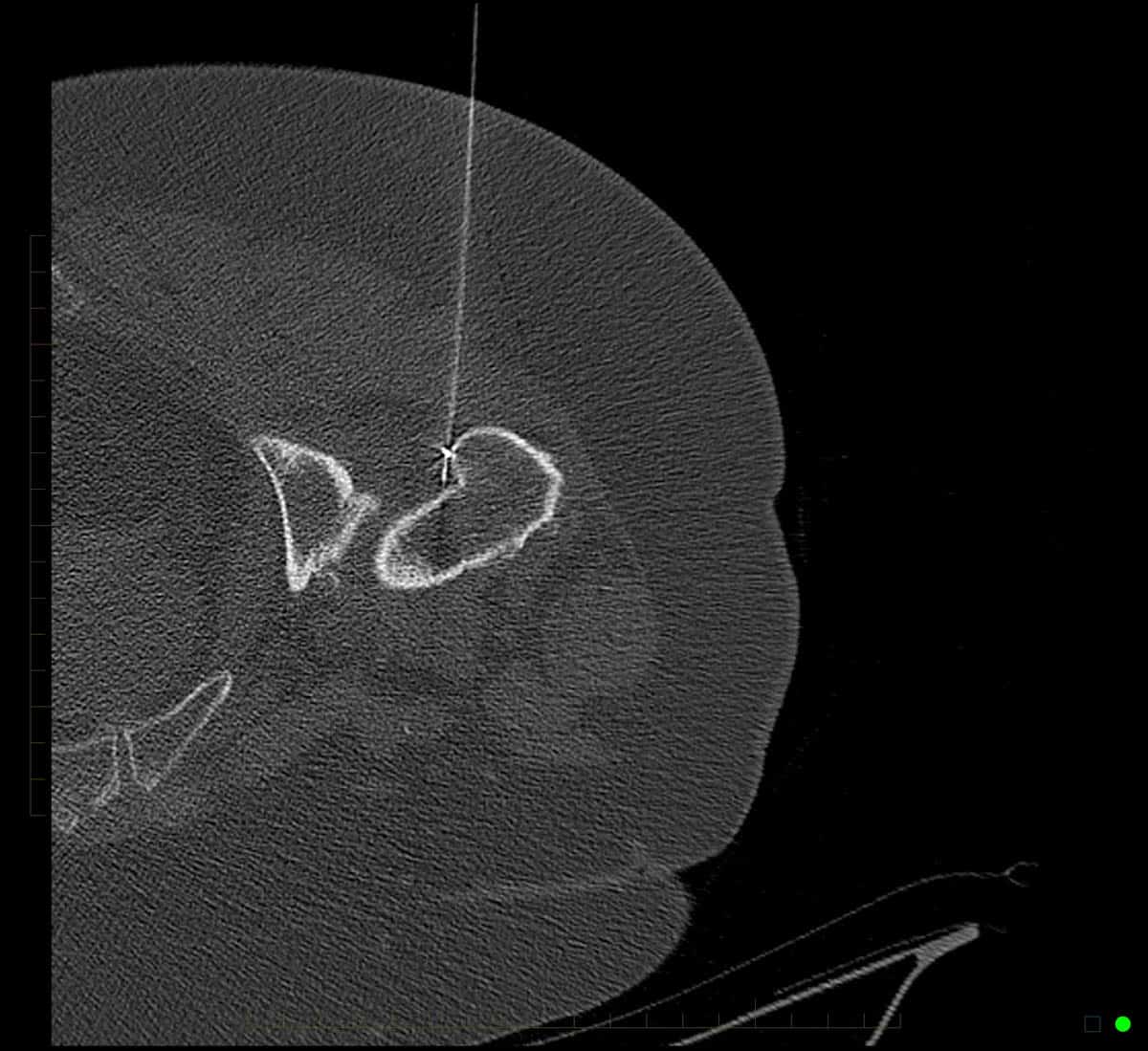
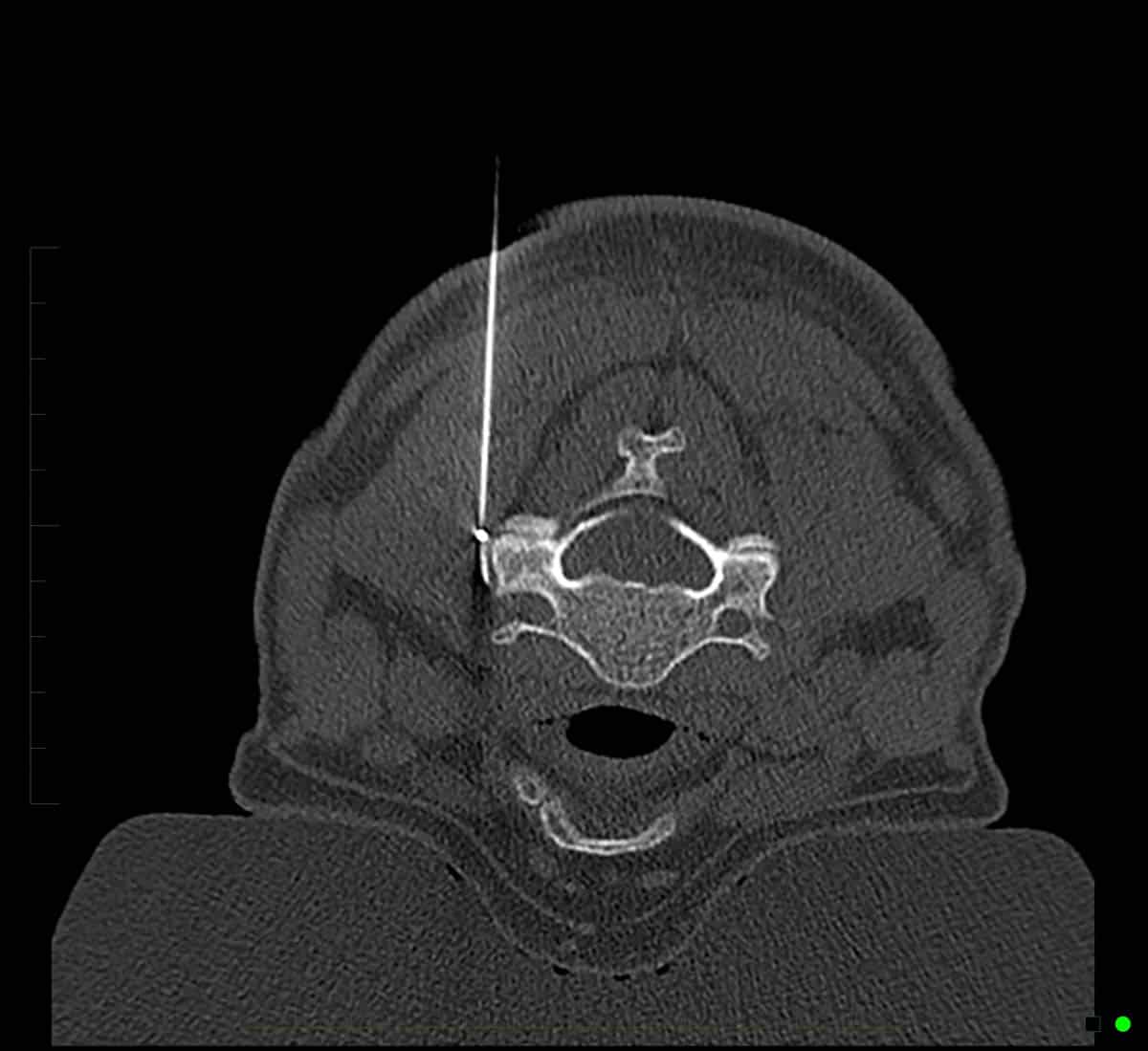
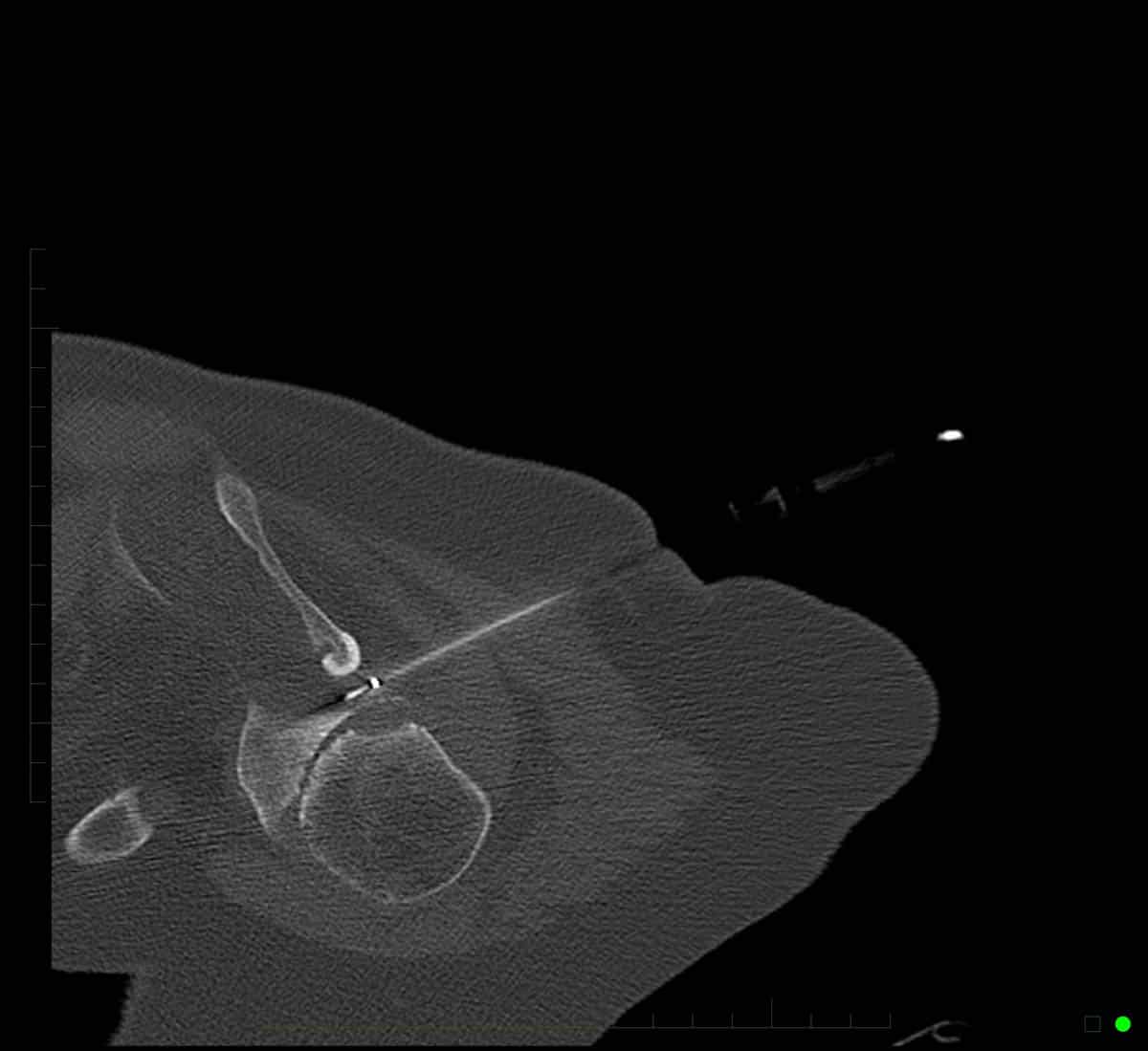
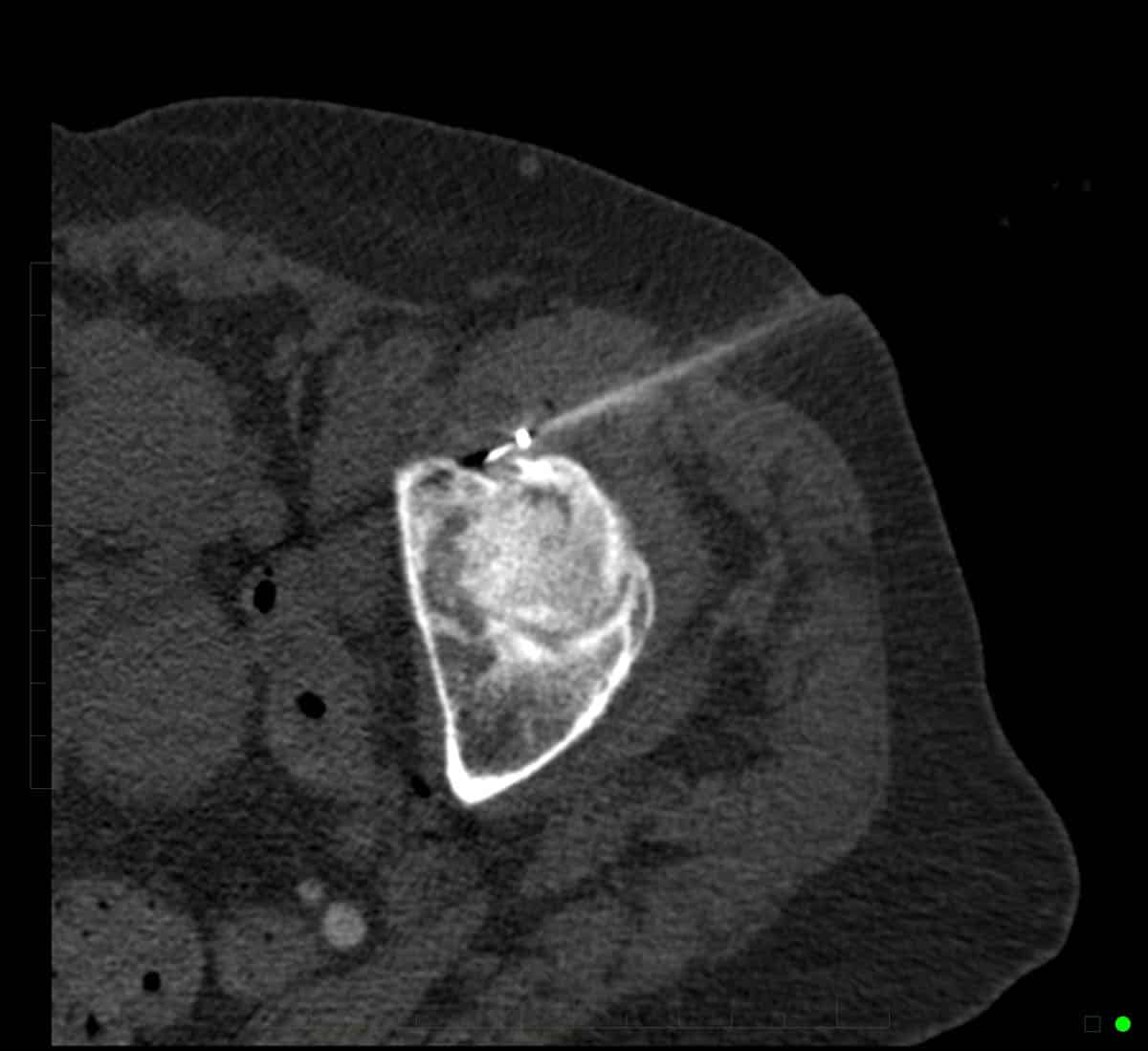
Radiofrequency ablation performed with CT imaging guidance to treat facet joint pain of lumbar spine.
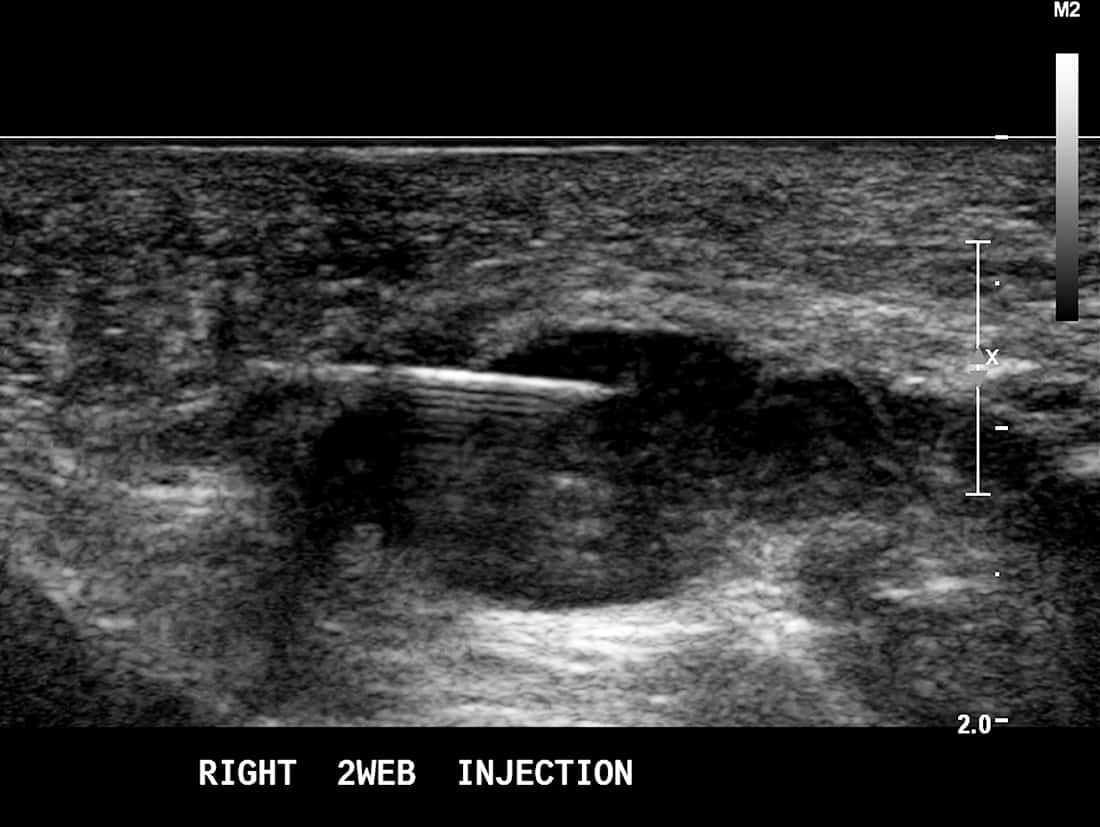
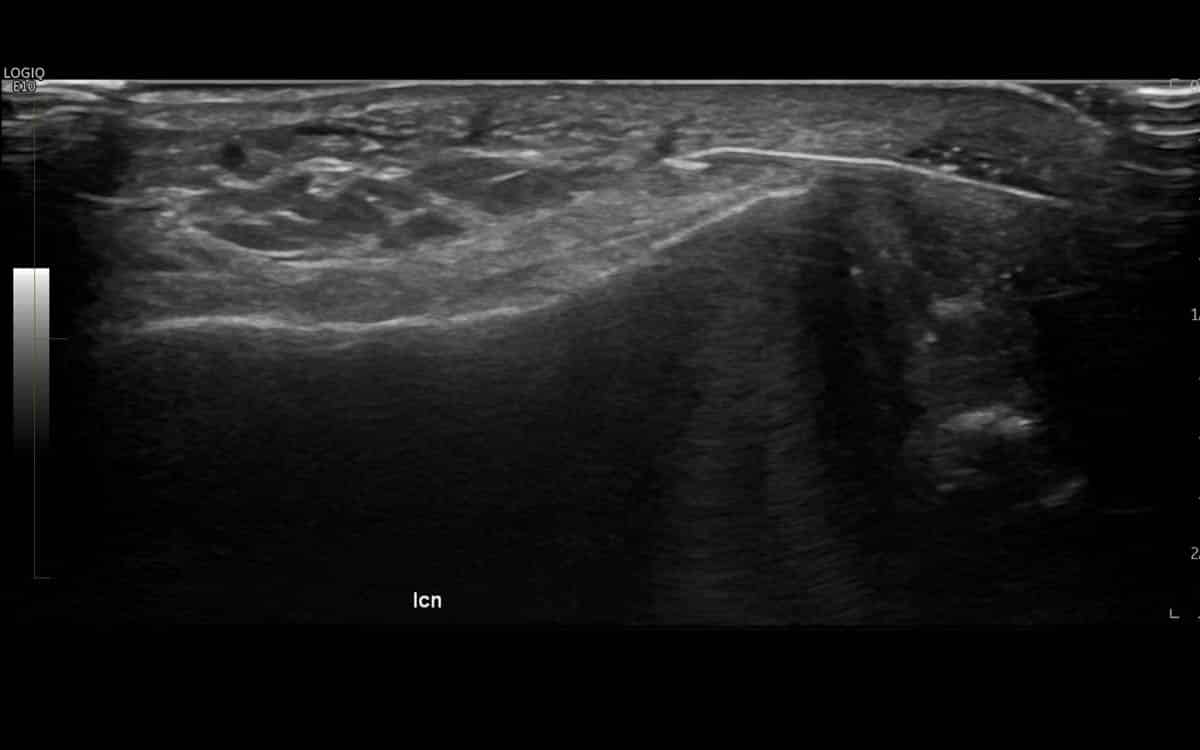
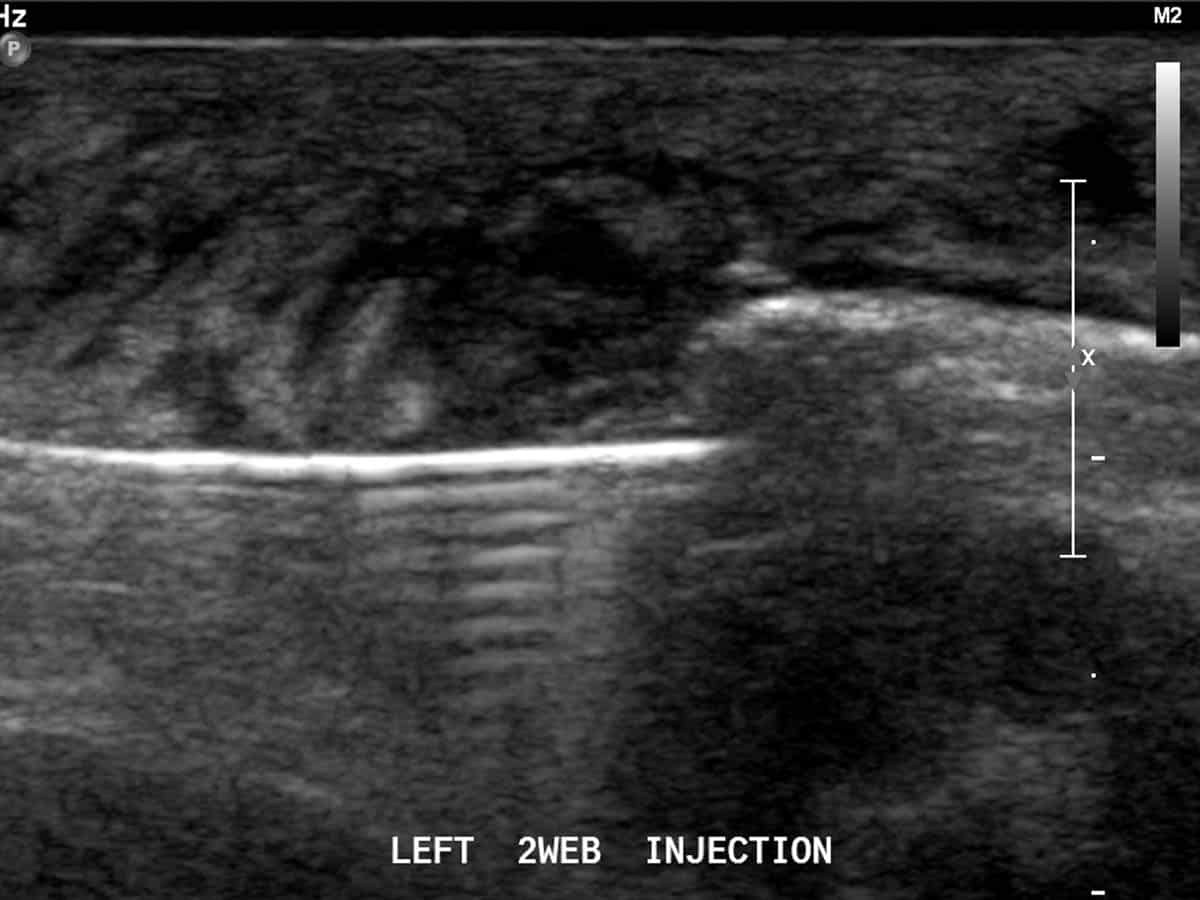
Ultrasound guided RFA to treat Morton’s neuroma.
RFA in pain management.
RFA can be used to treat back pain that is due to facet joint arthritis, recalcitrant heel pain due to plantar fasciitis as well as conditions such as Morton’s neuromas that causes disabling forefoot pain.
RFA can also be used to treat shoulder pain, recalcitrant knee and trochanteric region pain as well as post-operative neuromas.
Conditions treated
by RFA.
- Facetogenic cervical, thoracic and lumbar pain
- Sacroiliac joint pain
- Morton's neuroma
- Plantar fasciitis/fasciosis
- Tendinopathy
- Greater Trochanteric Pain syndrome - including gluteus minimus and medius tendinosis/tendinopathy and trochanteric bursitis
- Hip joint pain
- End stage knee arthropathy
- End stage shoulder arthropathy
- Meralgia paraesthetica (lateral femoral cutaneous nerve entrapment)
- Neuralgia/neuritis
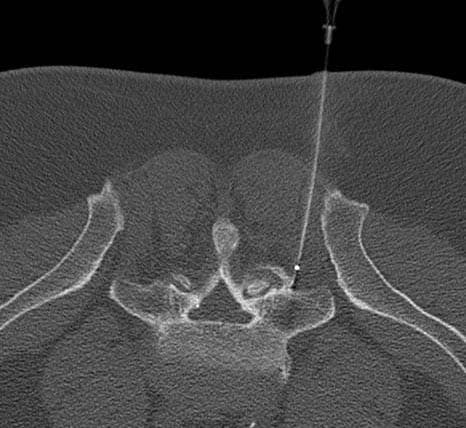
Radiofrequency Ablation – Performed with CT imaging guidance – right L5 medial branch
RFA is performed under image guidance
Depending on the location of the procedure, an ultrasound machine or CT (Computed Tomography) Scanner will be used to guide the procedure.
The procedure typically takes about 30 minutes, is performed under local anaesthetic and may result in discomfort for approximately a week after.
NOTE:
Due to the use of radiofrequency energy, the procedure can only be performed in patients with pacemakers where the pacemaker is permitted to be switched off once approved by a cardiologist. If the pacemaker cannot be temporarily switched off, then RFA cannot be performed.
Further Information.
Referring doctors are welcome to discuss with our radiologists the imaging and interventional radiology needs of their patients and whether radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is suitable for their patient’s medical condition.
Interventional Radiology Resources (PDF)