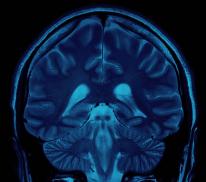
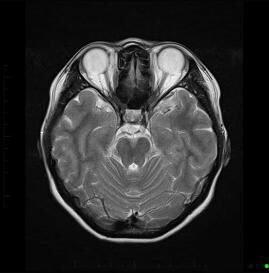
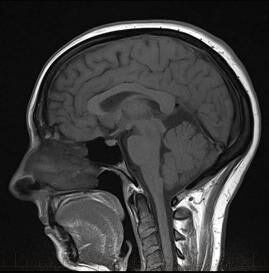
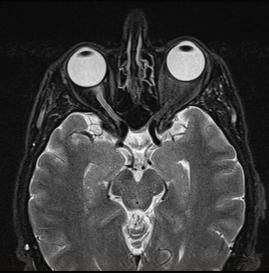
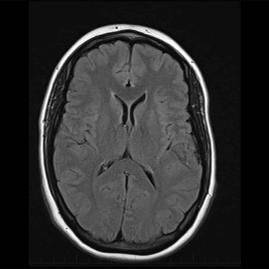
Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Brain.
MRI Head Scan.
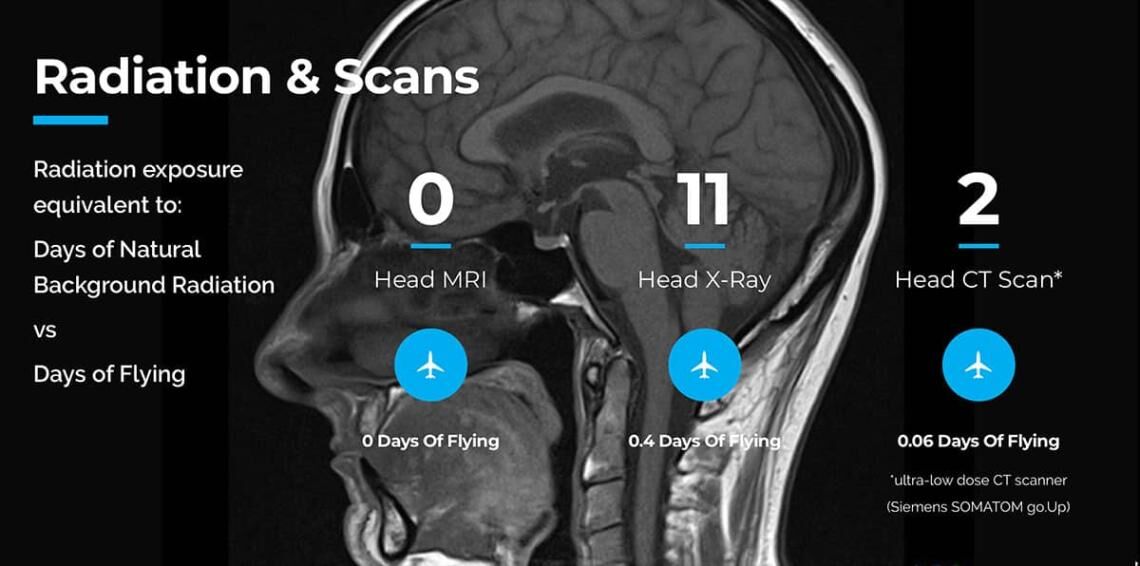
It is natural for patients to get nervous if their physician refers them for a MRI brain scan. Although the machine and procedure look and sound intimidating, the actual procedure is safe and painless. Unlike computed tomography (CT scans) or X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) tests do not use ionising radiation, which is why it is considered the best type of radiological imaging test.
This is also why MRI is particularly ideal in evaluating paediatric patients since it’s a non-invasive scan, and children’s organs can be more sensitive to radiation.
Due to the standard MRI machine’s narrow tunnel-like feature, claustrophobia and discomfort are common issues raised by patients undergoing the procedure. However, wide-bore MRI systems— the type of MRI machine Melbourne Radiology Clinic uses to conduct the scan— eliminates these issues, balancing efficacy, quality results, and patient comfort.
MRI Does Not Use Radiation
Noninvasive and radiation-free technology.
Unlike other imaging tests, MRI does not need radiation to perform the procedure. It also allows doctors to check for abnormalities, injuries, or diseases in the brain and other organs without surgery.
MRI scanners rely on large and powerful magnets. The magnetic field and radiofrequency waves manipulate the natural alignment of the body’s water molecules. Essentially, these pulses of radio waves from the scanner knock the nuclei in your hydrogen atoms out of their normal position, and when they realign, they emit energy.
This energy is then picked up by a coil as a signal, which is received by a computer that analyses and digitises it into an image.
Clear and Precise.
MRI is the most sensitive diagnostic imaging test of the brain in clinical practice, becoming a critical tool for diagnosing brain conditions.
As an extremely sensitive imaging scan, magnetic resonance imaging can differentiate between body tissue such as the grey and white matter of the brain. By providing clear and precise imaging of soft tissues, MRI has become an essential instrument for doctors to determine brain conditions and abnormalities.




Uses for MRI Scan - Brain.
MRI imaging allows doctors to examine blood flow and tissue health in certain brain structures. This enables them to check for medical conditions, such as brain tumours, cysts, multiple sclerosis, pituitary gland disorders, blood clots, aneurysm, and HIV infection of the brain.
Doctors may also refer patients to undergo this procedure to evaluate abrupt or long-standing symptoms like persistent headaches, dizziness, and seizures to determine the underlying health condition.
Further Information.
Referring doctors are welcome to discuss with our radiologists the imaging needs of their patients and whether MRI is suitable for their patient’s medical condition.
Specialist Radiologists.
MSK & MRI Fellowship Trained Radiologists