Ultrasound imaging for heel injuries.
Plantar fasciitis ultrasound.
Plantar fascia disorders are common among adults. They cause pain and disability that may curtail physical activities like sports, work, or even routine tasks.
Instead of a conventional radiograph or a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, an ultrasound is the preferred modality of imaging for assessing and treating plantar fascia cases due to its affordability and accessibility. It also provides physicians with rapid results and immediate medical corroboration of the deduced diagnosis.
Additionally, this imaging method allows the patient to move their foot and ankle while the doctor performs the examination. Ultrasound thus leads to a more accurate and pinpoint diagnosis of heel pain and aids in facilitating a more direct and appropriate treatment of the causal pathology.
No radiation.
An ultrasound is a non-invasive, radiation-free diagnostic imaging tool that uses inaudible sound waves to create images of internal body structures, including the plantar fascia within the foot. While MRI also does not utilise radiation for its procedure, an ultrasound is still the chosen tool for plantar fasciitis imaging because of its affordability and capability to provide far detailed information about the fascia fibres, among other things.
Real-time images.
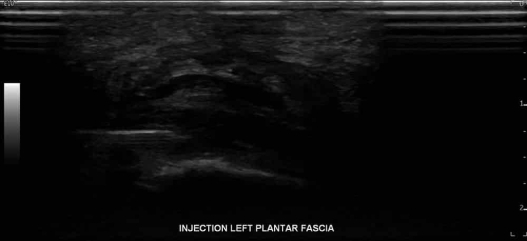
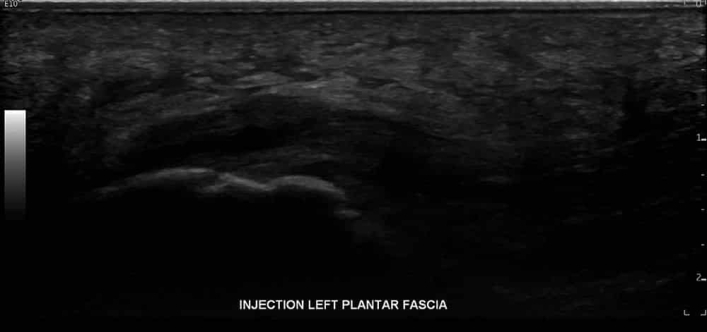
For the overall assessment and management of plantar fasciitis, physicians will use ultrasound for particular reasons: first, to dynamically move the affected region during the examination. Second, due to providing real-time images of the heel’s internal structure, ultrasounds are excellent tools during response treatments to ensure doctors accurately place the injection on the most damaged region. It is in this way that they can facilitate better outcomes for the patient.
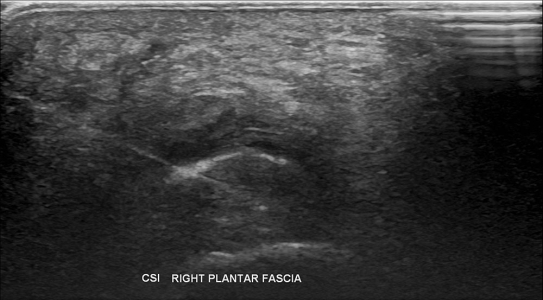
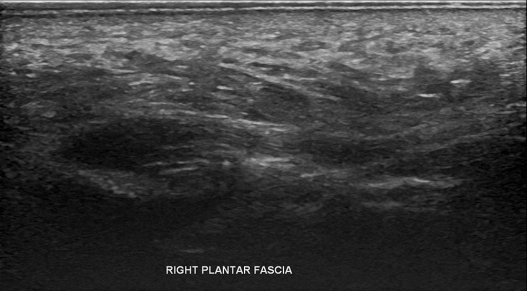
Understanding plantar fascia tear ultrasound.
Plantar fasciitis ultrasound observations show the thickening of the fascia over 4mm and a hypoechoic fascia. Diagnosis is made easier with sonographic machines as they enable marking and measuring of the fascia. Thickness decreases on ultrasound with successful treatment.
Other plantar fascia tear ultrasound findings include the loss of fibrillar structure, perifascial collections, calcifications, and soft tissue abnormalities. Hyperaemia can also be revealed through doppler ultrasound.
Further Information.
Referring doctors are welcome to discuss with our radiologists the imaging needs of their patients and whether an ultrasound is suitable for their patient’s medical condition.
Specialist Radiologists.
MSK & MRI Fellowship Trained Radiologists