Shoulder Hydrodilatation
Adhesive capsulitis, or frozen shoulder is a condition of the shoulder which results in the formation of inflammation and the subsequent production of scar like tissue in the shoulder joint to result in pain, stiffness and debility. The condition is common in diabetics and in this particular group, it may be recalcitrant, often requiring several injections.
Frozen Shoulder Radiology
Adhesive Capsulitis (frozen shoulder) is a condition that results in pain and limited mobility in the shoulder. Although the cause is often unknown, certain other issues seem to make sufferers more prone – recent trauma, surgery, diabetics, stroke and occasionally even a heart attack.
The diagnosis can be difficult to make both clinically and radiologically. The capsule (or covering) of the shoulder becomes inflamed, such that scar tissue forms and therefore results in the sensation of stiffness/decreased mobility. The process of freezing, frozen, and thawed adhesive capsulitis (all terms to describe the progress of the problem) can take few months to two years to resolve spontaneously, however considering how debilitating the condition may be, then radiologically guided treatment may ultimately be required.

Shoulder Joint Radiology – Diagnosis and Treatment
Though the diagnosis is typically made by clinical assessment, imaging is often utilised to confirm the diagnosis, as well as to exclude other potentially co-existent diagnostic possibilities. MRI, CT scans and ultrasounds can therefore be used, with MRI being the most accurate modality to diagnose adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder).
Frozen Shoulder Radiology Treatment
The treatment at frozen shoulder radiology involves injecting a solution of cortisone and saline directly into the shoulder capsule, known as hydrodilatation and is typically performed under CT guidance.
The cortisone is used to suppress inflammation while the saline stretches the scarred capsule, the latter often allowing for a rapid improvement in range of motion.
As frozen shoulder is a potentially a long-term issue, a repeat injection may be required.
Shoulder joint radiology can also be used to detect and treat other shoulder disorders, such as rotator cuff degeneration as well as arthritis of the joint. These conditions can be accurately diagnosed using radiology.
If you require any healthcare imaging services or radiological examinations including MRI or X-ray for shoulder injuries, MRI for ankle injury & knee MRI scan procedures then contact the team at Melbourne Radiology Clinic. We accept referrals from all over Melbourne – any written referral can be used, even if it is for another radiology provider. To book, call our reception staff on (03) 9667 1667. Alternatively, email to info@melbourneradiology.com.au, including your referral, if you have been provided with this, or you can use our online booking form to get in contact and we can call you back to book you an appointment.
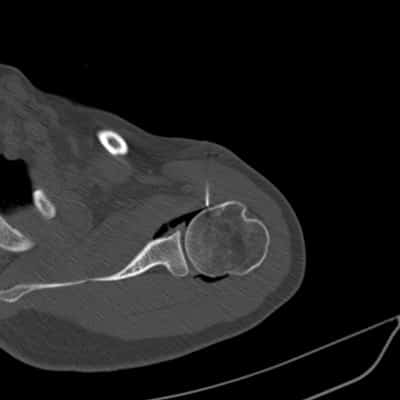
Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder
Adhesive capsulitis has been reported to be a self limiting disease, meaning that untreated, it will eventually spontaneously improve, however this may take up to 2 years.
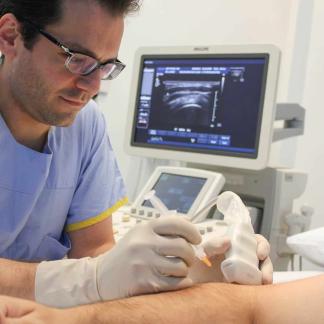
In its early phase, the disease may result in vague shoulder pain which mimics other causes of shoulder pain. The diagnosis is often suggested at the time of ultrasound evaluation, when patients are unable to move their shoulder in the necessary positions required for the scan. An ultrasound also yields important information, as it may diagnose the underlying cause that resulted in the patient developing adhesive capsulitis in the first instance.
Common causes of adhesive capsulitis
The cause of adhesive capsulitis is often not known. However, when known, common causes include:
- Rotator cuff tendinosis/tendon tears
- Subacromial Bursitis
- Shoulder surgery
- Trauma Shingles
- Heart attack, chest surgery and stroke
Treatment of adhesive capsulitis
In mild cases, adhesive capsulitis usually responds to rehabilitation. If the condition progresses, often an injection, called a hydrodilatation (or hydrodilation) using cortisone and saline is required to suppress the inflammation and thus target the underlying disease process.
The joint is then stretched with approximately 20-40mls of saline, often resulting in a popping sensation. It is debatable whether stretching the capsule with the addition of saline is of additional benefit and makes the procedure more painful. It is felt that the stretching part of the procedure tears the scarred capsule of the joint to improve mobility. Whether this is of additional long term benefit is as yet unproven, however stretching the capsule can often result in immediate improvement of a patient’s range of motion.
Patients may require several injections to treat the condition, however if this is unresponsive, then another option includes manipulation under general anesthesia and surgery.
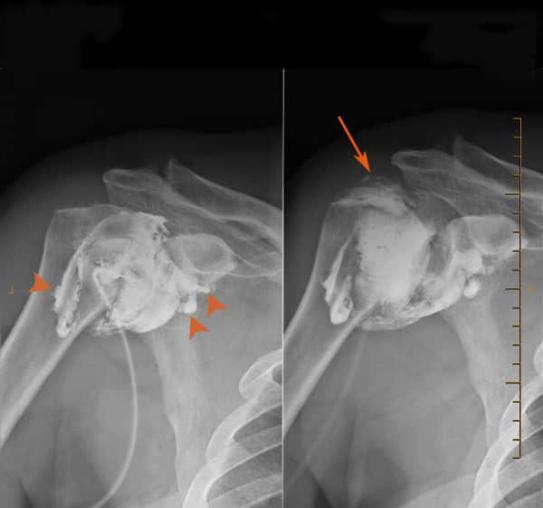
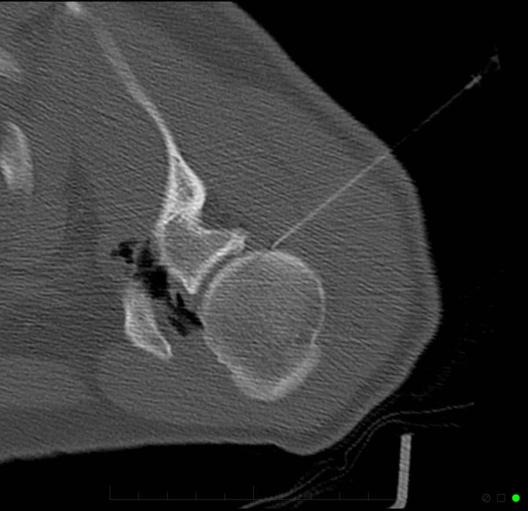
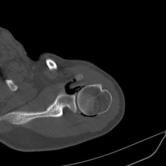
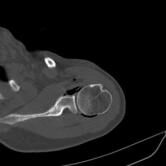
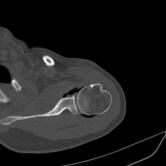
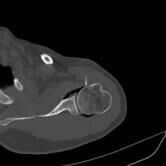
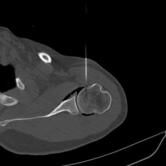
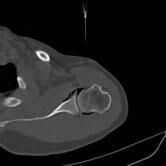
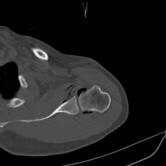
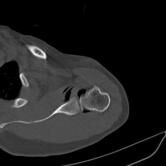
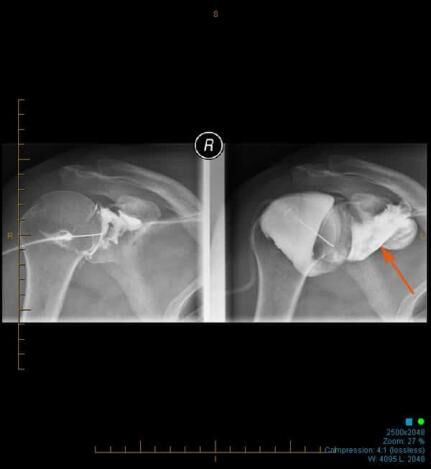
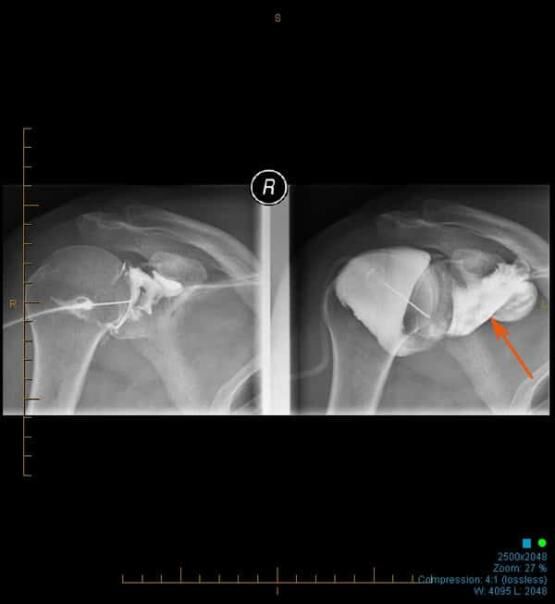
CT Guided Hydrodilatation
The skin is marked for accurate needle placement (image 1 of 9), with a needle then introduced into the shoulder joint.
Gas is then introduced into the joint to confirm position, with the medication then injected to relieve the patient of their adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder).
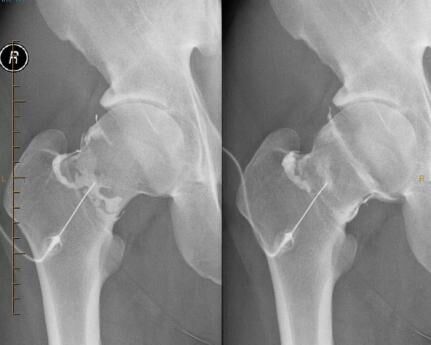
Arthrogram
Diagnostic &/or pain relieving procedure
An arthrogram is a procedure performed at Melbourne Radiology Clinic where imaging guidance (with either an ultrasound or CT) is used to guide a needle into a joint for the purposes of injecting X-ray and/or MRI dye (contrast). The contrast in the joint then preferentially fills different parts of the joint and may give further clues as to the source of the patient’s symptoms, such as pain. Typically large joints, such as the hip and shoulder undergo evaluation with an arthrogram, especially following surgery.
If used solely as a pain relieving procedure, local anaesthetic and cortisone may be injected, or other healing medications, such as glucose (prolotherapy), Autologous Blood Injection (ABI) or Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP).
An arthrogram may also be of diagnostic use. Pain that disappears following an injection of local anaesthetic into a joint usually confirms that the joint injected is the source of the patient’s pain. As groin pain has many causes, this technique is commonly used in deciding whether the hip joint is the cause of a patient’s groin pain. Though this may narrow the source of the patient’s pain, it does not determine the exact cause. For this, further imaging is usually required, such as an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) or CT (Computed Tomography) scan. If these scans are to be performed on the same day as the arthrogram, the fluid and dye injected into the joint not only may relieve the patient’s pain, but also distends the joint and makes subtle problems more evident, such as a cartilage tear.
FAQ
Is hydrodilatation painful?
The level of discomfort from hydrodilatation varies, depending on the degree of associated inflammation and restricted movement, although the overall procedure is tolerable and takes only about 15 to 30 minutes. There may also be some pain in the injected area that lasts for a few days to one week.
How long does hydrodilatation take to work?
Many patients have reported immediate pain relief right after the hydrodilatation shoulder procedure. Benefits include a decrease of pain in the shoulder and increased joint movement. However, for some people, it can take a few days to a couple of weeks to feel the effects, with the aid of physiotherapy.
What is the fastest way to heal a frozen shoulder?
Besides a hydrodilatation injection, the fastest way to treat a frozen shoulder is physical therapy. Your physiotherapist will focus first on exercises that stretch the joint capsule before moving on to strengthening workouts.
For temporary relief, take anti-inflammatory medications such as aspirin or ibuprofen, or apply an ice pack to the shoulder for 10 to 15 minutes several times a day.
What is the best exercise for shoulder pain?
Exercises that can be helpful for frozen shoulders include pendulum stretches, towel stretches, finger walk, cross-body reach and armpit stretch. Make sure to warm up before performing any exercises by taking a warm bath or shower for 10 minutes, for example. Alternatively, you can also use a heating pad or warm, damp towel in place of a bath.
Can you drive after hydrodilatation?
It is advised to have someone drive you home or take public transport instead of driving. If you have to drive, wait for 30 minutes after the hydrodilatation shoulder procedure before doing so. It is also recommended to refrain from operating heavy machinery for at least six hours.
References:
- Tveit EK, Tariq R, Sesseng S, Juel NG, Bautz-Holter E. Hydrodilatation, corticosteroids and adhesive capsulitis: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 19;9:53 2008
- Bell S, Coghlan J, Richardson M. Hydrodilatation in the management of shoulder capsulitis. Australas Radiol 47(3):247-51, 2003
- Watson L, Bialocerkowski A, Dalziel R, Balster S, Burke F, Finch C. Hydrodilatation (distension arthrography): a long-term clinical outcome series. Br J Sports Med 41(3):167-73, 2007
Further Information.
Referring doctors are welcome to discuss with our radiologists the imaging and interventional radiology needs of their patients and whether a hydrodilatation or arthrogram is suitable for their patient’s medical condition.